According to phonecations.com, the basilar thrombosis is caused by calcified arteries. An immediate medical indication is extremely important, as a basilar thrombosis is life-threatening. The basilar thrombosis is a special form of the insult (stroke).
What is a basilar thrombosis?
This special form of stroke primarily affects the brain. The so-called brainstem infarction often occurs directly in the center of the brainstem, which regulates the state of consciousness of the person as well as his breathing control.
Because of these factors, a basilar thrombosis is life-threatening and must be treated immediately. As with a stroke, the same applies here: the earlier the treatment, the better the chances of success of a complete recovery. Thus, at the first sign of a basilar thrombosis, the patient should not hesitate and seek immediate medical attention.
Causes
One of the main reasons why a basilar thrombosis occurs in the first place is arteriosclerosis. Atherosclerosis is a classic calcification of the arteries. If the patient suffers a basilar thrombosis, one of the two (or both) vertebral arteries of the brain stem is affected by the calcification.
This calcification results in a restriction in the blood supply, which subsequently leads to a brainstem infarction. The doctor speaks of a basilar thrombosis when one of the two (or both) vertebral arteries is blocked, a blood clot forms and the brainstem infarction is triggered. The locked-in syndrome is considered to be most severe form of the infarction.
Classic symptoms are symptoms of paralysis all over the body and disorders of sensitivity. The patient also complains of sensory disturbances and difficulty swallowing. Due to the fact that the infarct occurs in the center of the respiratory control, the patient suffers from breathing difficulties and complains of increasing shortness of breath. Furthermore, disorders of consciousness and speech disorders occur.
Symptoms, ailments & signs
A basilar thrombosis can lead to very serious and dangerous symptoms. As a rule, those affected suffer from disorders of consciousness, which in the worst case can also lead to a coma. In the event of a loss of consciousness, the person concerned can also injure himself if he falls.
Even swallowing, blurred vision or double vision pass through the basilar thrombosis often and complicate the patient’s life tremendously. This disease can also lead to speech disorders or paralysis of the extremities. Many patients also suffer from vomiting or nausea and thus from severe weight loss.
In the further course of the disease there are severe breathing difficulties, from which the affected person can die in the worst case. Most patients also experience dizziness and eye tremors. As a result, they are often dependent on the help of other people in their everyday life and can no longer do many everyday things on their own.
Psychological complaints can also occur due to the basilar thrombosis, whereby the parents or relatives can also be affected by these complaints. If left untreated, the basilar thrombosis leads to death. The breathing difficulties can also permanently damage the internal organs or the brain.
Diagnosis & course
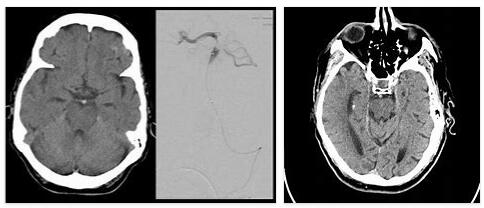
If a basilar thrombosis is suspected, the doctor will order a computed tomography – CT scan. This diagnostic method is intended to provide information about whether a brainstem infarction is present. Computed tomography of the skull is also often referred to as “cranial computed tomography”.
The use of magnetic resonance tomography is also possible; However, this is only rarely used – as part of the diagnosis of a basilar thrombosis. Another option is the MR angiography procedure. With this method it is possible for the physician to localize the site of the infarction by means of imaging diagnostics. The course of the basilar thrombosis depends primarily on how severely the patient is affected by the infarction. It is very likely that mild, but also very severe, brainstem infarctions apply.
Rehabilitation measures are also necessary so that the patient can master his old skills again or, if necessary, learn again. With a slight heart attack – such as Wallenberg syndrome – an independent life is possible again after rehabilitation. If the patient suffers a severe brainstem infarction, this can sometimes lead to long-term restrictions and permanent damage. Movement restrictions often remain as a long-term consequence.
Complications
As a rule, a basilar thrombosis is an insult that can be life-threatening for the human body. Without treatment, the patient can die in the worst case. This leads to severe disturbances of consciousness, loss of consciousness or even a coma.
The patients suffer from severe visual disturbances and nausea. In certain parts of the body paralysis and therefore severe restrictions on movement occur. The paralysis can also affect breathing, causing breathing disorders and panic attacks. Often the basilar thrombosis is accompanied by dizziness and vomiting.
The patient’s everyday life is severely restricted and the quality of life is greatly reduced. It is no longer possible for the patient to perform any physical activity. Treatment of the basilar thrombosis must be quick and usually takes place as an operation. After the operation, a long rehabilitation phase is necessary for the person affected, as this often leads to paralysis or damage to individual parts of the body.
Physiotherapy measures can alleviate these complaints or symptoms. However, it cannot be predicted whether all symptoms will completely disappear again, as some damage to the body is irreversible.
When should you go to the doctor?
At the first signs of a basilar thrombosis such as dizziness and vomiting and the simultaneous occurrence of neurological problems such as clouding of consciousness, visual and speech disorders as well as paralysis with breathing disorders, the question of whether a doctor should be consulted does not arise right from the start. It is imperative to see a doctor! There is an immediately life-threatening situation that requires immediate treatment in a specialist clinic.
If the necessary systemic dissolution or surgical removal of the thrombus, which is blocking the basilar artery and causing a brainstem infarction, does not take place immediately, the situation is acutely life-threatening and has a very poor prognosis.
For acute treatment, clinics are suitable which, for example, can localize thrombi in the brain and dissolve or surgically remove the thrombus with systemically effective means or by means of locally effective methods. If the dissolution or removal of the thrombus is successful, an attempt is made to get back as close as possible to everyday life with rehabilitation measures.
Some of the rehabilitation measures are comparable to those used after a stroke. To avoid a recurrence of the thrombosis, regular examinations or examinations of important arteries for arteriosclerosis should be carried out in a clinic or doctor’s office that has a suitable sonography device. In order to keep the risk of arteriosclerosis low, we recommend a diet that is as natural as possible and that is suitable for keeping the ratio of the LDL fraction to the HDL fraction of total cholesterol below 3.5.
Treatment & Therapy
Before treating the brainstem infarction, it is important that the treatment begins as soon as possible. Depending on the type and severity as well as the form of the infarction, the doctor decides on the treatment method. Another reason for making a decision is the physical condition of the person concerned.
If the vertebral arteries are occluded and the brainstem infarction ensues, local thrombolysis is usually used. The doctor uses the lysis to dissolve the blood clots in the arteries. This is where drugs are used to loosen the clot. Another alternative is surgery. Here the doctor removes the blood clots on an operative basis.
If the patient complains of swallowing difficulties or shortness of breath, it is often necessary for the doctor to insert a nasogastric tube. Long-term ventilation can also be used. Many experts believe that patients who have had a brainstem infarction should be treated at a medical center. Above all, rehabilitation and therapy should be carried out in such a specialist center; here there is a higher success rate for faster or complete healing of the patient.
After brainstem infarction treatment, it is important that consistent therapy take place. This is used in the form of physiotherapeutic measures and exercises. This is intended to remedy any restrictions on movement so that the patient does not suffer any permanent damage. However, appropriate therapy often takes months.
Outlook & forecast
The prognosis depends on the type and severity of the basilar thrombosis. There is rarely a complete recovery and freedom from symptoms. Most patients suffer from lifelong complications and need long-term therapy.
The basilar thrombosis must be treated immediately by intensive care. Without treatment, the patient will die within the next few hours or days. The later a diagnosis is made and the start of treatment, the worse the chances of recovery. In addition, the patient’s age and health are essential for the healing process. Middle-aged people with no other illnesses and stable immune systems have the best chance of a cure if treated as quickly as possible.
In most cases, despite all efforts and immediate medical care, various functional disorders persist for a long time after the basilar thrombosis. Paralysis, language disorders and severe impairments in coping with everyday life occur. The patient is often dependent on daily help and can no longer go about his usual work.
Therapy of the patient after survival of the basilar thrombosis is individual and depends on the sequelae. In most cases, it takes several years for the patient to be able to carry out many of the usual activities again. Some of them he will never do again.
Prevention
The patient can only prevent a basilar thrombosis to a limited extent. Ultimately, arteriosclerosis, the calcification of the two arteries, must be prevented or combated. This means that the patient has to go to regular examinations to clarify the situation.
Above all, overweight people who suffer from high blood pressure and have an unhealthy lifestyle are usually affected by arteriosclerosis. Especially high-risk patients should therefore regularly go to a medical check-up to prevent the basilar thrombosis.
You can do that yourself
The basilar thrombosis can be viewed as a special form of stroke. When one or both of the basilar arteries, which supply the brainstem, including the respiratory center, with oxygen and nutrients, are blocked by a blood clot, a brainstem infarction is caused, with serious consequences in some cases.
In the acute case, there are no known self-help measures that could prevent the effects from worsening, because in the acute case the focus is exclusively on diagnostic measures for the precise localization of the thrombus and its dissolution through thrombolysis or surgical removal, so that the corresponding brain regions are supplied with oxygen again will.
It is obvious that the basilar thrombosis must be treated as quickly as possible because the effects – if left untreated – quickly become greater and then usually turn out to be irreversible. The prognosis in the event of non-treatment is very unfavorable and also does not rule out fatal consequences. Depending on the severity of the damage caused by the infarction, adjustments in everyday life and self-help measures are required.
The self-help measures mainly consist of support for rehabilitation in consultation with the physiotherapist and the treating doctor. The exercises to be used are individualized and in some cases comparable to exercises that are available for selection after a classic stroke. They serve to get as close as possible to the previous everyday life, if that can be a realistic goal at all.