If the doctor speaks of a urea cycle defect, he uses an attack that mainly affects several metabolic diseases, which on the one hand have a genetic origin and on the other hand are responsible for a disturbed nitrogen excretion. If left untreated, the urea cycle defect leads to the death of the patient. Liver transplantation is the only form of therapy to correct the urea cycle defect.
What is a urea cycle defect?
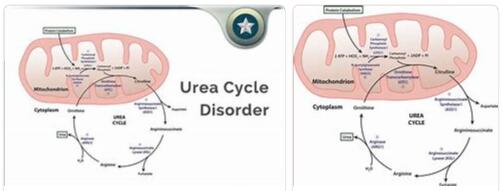
According to abbreviationfinder.org, an urea cycle defect usually serves as an umbrella term for several metabolic diseases, all of which have a disturbed nitrogen excretion. Another common feature is the genetic origin; such metabolic diseases can therefore be inherited.
Since a urea cycle defect leads to a pathological increase in the neurotoxin ammonia, the disease leads to brain damage and death if not treated in time. It should be noted that there are six different enzyme defects. The symptoms can vary depending on age and initial manifestation.
Causes
Urea cycle defects are inherited in an autosomal recessive manner. The only exception is the OTC shortage; OTC deficiency is inherited exclusively in an X-linked recessive manner. Spontaneous mutations can sometimes occur. This means that the urea cycle defect is not inherited, but that the genetic defect arose spontaneously.
Urea cycle defects are therefore congenital metabolic diseases of the liver that are potentially life-threatening. This not only leads to an increase in the ammonia level, but also to a disturbed breakdown of protein. Due to an existing deficiency of certain enzymes, the body is not able to subsequently convert ammonia, a toxic intermediate, into urea.
This inevitably leads to an increase in the ammonia level, with the neurotoxin being stored in the blood and other tissues. There is a risk of brain and nerve damage; sometimes the disease can lead to the death of the patient.
So far, six enzyme defects are known to be responsible for a urea cycle defect:
- Carbamyl phosphate synthetase (CPS)-1 deficiency
- Ornithine transcarbamylase (OTC) deficiency
- Argininosuccinate synthetase (ASA) deficiency (citrullineemia type 1)
- Argininosuccinate Lyase (ASL) Deficiency ( Argininosuccinic Acid Disease )
- Arginase 1 deficiency (hyperargininemia)
- N-acetylglutamate synthetase (NAGS) deficiency
It has not yet been possible to clarify why such deficiencies occur.
Symptoms, Ailments & Signs
The symptoms vary depending on age and initial manifestation. They are therefore mainly based on the age of the person concerned. In infancy, vomiting, an extremely high respiratory rate, seizures and reduced fluid intake are possible. At times, the infant may go into a coma.
Seizures occur again and again in infancy; behavioral disorders, growth deficits and reduced food and liquid intake were also observed. Even in infancy there is a risk that the patient will fall into a coma.
The following symptoms occur mainly in adolescents and adults: Those affected are irritable, lethargic, often confused, suffer from nausea and vomiting again and again and feel listless. In severe cases, patients can also fall into a coma. Depending on the clinical picture, the symptoms can vary. On the one hand they can be particularly intense, but on the other hand they only occur slightly.
Diagnosis & History
If there are occasional complaints that indicate a urea cycle defect, laboratory tests are carried out. Doctors determine an excessive level of ammonia in the blood. The diagnosis can be substantiated, for example by a genetic test, in which the identification of the mutation is checked.
Severe disease progressions result primarily from defects in the first three enzymes. Basically, the enzyme deficiency is subsequently responsible for the course of the disease that must be feared. Higher residual activities usually lead to chronic forms, which only become noticeable after the neonatal phase.
If the urea cycle defect is treated incorrectly or not at all, brain and/or nerve damage will inevitably result. As a further consequence, an untreated urea cycle defect leads to the death of the person concerned. It does not matter which enzyme defect is present. All enzyme defects, if left untreated, can lead to death.
Complications
If left untreated, the urea cycle defect leads to the death of the patient in most cases. For this reason, urgent treatment of this disease is necessary for the patient. This also avoids complications and consequential damage. The person affected usually suffers from nausea and vomiting due to the urea cycle defect. There are also cramps, which are associated with severe pain.
Gasping occurs and panic attacks are not uncommon. Likewise, the person affected may lose consciousness or even fall into a coma. It is not uncommon for those affected to suffer from behavioral disorders, which can have a negative impact on development, especially in children. The patients are usually confused and slightly aggressive. Difficulty sleeping can also lead to slight irritability.
If the defect is not treated, in most cases the life expectancy of the patient is greatly reduced and ultimately death. The treatment itself does not lead to further complications. However, the affected person may need dialysis for a liver transplant. In most cases, the other symptoms depend on the underlying disease.
When should you go to the doctor?
Since the urea cycle defect can lead to death in the worst case, it must be treated by a doctor. Self-healing does not occur in this disease. The urea cycle defect can occur in children or infants. It leads to vomiting or a high breathing rate.
If the parents notice these symptoms, a doctor should be consulted. Complaints and irregularities in growth also indicate the disease. The disease also leads to seizures or difficulty drinking. Those affected suffer from behavioral problems and are often aggressive or irritable.
Confusion also often points to the urea cycle defect. The severity of the symptoms can vary greatly, so that they do not always have to be a symptom of the defect. However, since the disease can only be cured by liver transplantation, an examination should always be carried out as a precaution if the symptoms mentioned are noticed.
As a rule, the urea cycle defect can be diagnosed by an internist. The treatment then takes place with the help of a surgical procedure in a hospital. It cannot generally be predicted whether the course of the disease will be positive.
Treatment & Therapy
When it comes to treatment options, there are several therapies available. In the case of a neonatal disease manifestation that poses a threat to the life of the infant, intensive care treatment is initiated. Such treatments, which are also referred to as acute therapy, mainly take place in metabolic centers.
The goal of such therapies is to lower toxic ammonia levels. The ammonia level is reduced by dialysis, for example, whereby the “blood wash” is only carried out when the ammonia concentration is over 400 µmol/l. The infants do not receive proteins; sometimes medications are administered to help reduce blood levels of ammonia.
Sometimes liver cell therapy can also lead to success. Such therapies are mainly recommended for infants; Even if liver transplantation would be more effective, the procedure is extremely stressful for the newborn, so many doctors refrain from it. The risk that the child will not survive the procedure is too high in almost all cases.
In liver cell therapy, adult hepatocytes are obtained from the donor liver and then – free of bacteria – cryopreserved in a suspension. In the long run, medical professionals opt for dietary and drug treatment. It should be noted that this treatment must be carried out for a lifetime.
The only actually curative therapy that sometimes eliminates the urea cycle defect is liver transplantation. The urea cycle defect can only be eliminated if a liver transplant is carried out.
Outlook & Forecast
In many cases, being diagnosed with a urea cycle defect does not lead to a normal life. The disease causes limitations in everyday life. Only a long-term treatment can justify the greatest possible freedom from symptoms. Those affected must expect restrictions in their diet when the hereditary disease occurs.
Blood washing and drug administration accompany life. A cure is impossible. If the defect is not recognized in time, brain damage usually occurs. Eventually, the urea cycle defect leads to death.
Statistically speaking, the disease occurs more frequently in certain phases of life. This is where the greatest risk prevails; However, the urea cycle defect is a marginal phenomenon in relation to all persons of a cohort. Boys and girls in infancy and childhood are particularly affected.
About 50 percent of all diseases can be attributed to this age group, which corresponds to just 80 newborns per year in Germany. Occasionally, women also become ill during pregnancy. Basically, cases of persons of legal age have a marginal character.
Long-term therapy aims to keep blood levels of ammonia and glutamine within the normal range. This is achieved by adhering to a constant low-protein diet. If this procedure is followed, one can lead a symptom-free life. Patients have to show a high degree of discipline for this.
Prevention
Since a urea cycle defect is a genetic disease whose origin is unknown and which is usually inherited or caused by spontaneous mutation, the metabolic disease cannot be prevented.
Aftercare
Since a urea cycle defect cannot heal itself and the disease is a genetic disease, the options for aftercare for this disease are severely limited in most cases. The affected person is primarily dependent on a quick diagnosis with subsequent treatment so that the symptoms do not worsen further.
In the worst case, the patient can die if the disease is left untreated. Patients are often dependent on dialysis measures. They also need the care and support of their own family and friends. This can also alleviate or completely prevent psychological upsets or depression. When taking medication, patients should ensure that they are taken regularly and that the dosage is correct in order to alleviate the symptoms.
A healthy lifestyle with a balanced diet can also have a positive effect on the course of this disease. If the affected person wishes to have children, genetic counseling is advisable in order to prevent the disease from recurring in the children. The patient’s life expectancy may be reduced as a result of the disease.
You can do that yourself
A urea cycle defect is a serious disease that often takes a negative course. The most important self-help measure is to inform the responsible doctor immediately about unusual symptoms or to take the child to the nearest hospital. If a metabolic disease is actually present, treatment must be initiated immediately in order to avoid consequential damage.
The individual symptoms can be treated with the known means and measures. Dietary measures as well as bed rest and rest help against nausea and vomiting. Cramps can be relieved by calming down and using medicinal preparations. If the child shows signs of a panic attack or even becomes unconscious, an ambulance must be called.
In the case of behavioral disorders, behavioral therapy makes sense, and the parents should also take part in it. Comprehensive training can be used to react optimally to irritability, aggressiveness and other abnormalities, which at least reduces the risk of developmental disorders.
In the long term, a therapeutic consultation is also useful. In many cases, the disease leads to the death of the patient – a circumstance that represents an enormous burden for the affected child, but also for the relatives.